Unlock the secrets to understanding, managing, and preventing the “silent killer” for a healthier, longer life.
Did you know that nearly half of adults in the United States have high blood pressure, and many don't even know it? This common condition, medically known as hypertension, is often called the "silent killer" because it typically has no warning signs or symptoms. Yet, when left uncontrolled, it quietly damages your blood vessels and significantly increases your risk for severe health problems like heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. Understanding **high blood pressure** is the first, most crucial step toward taking control of your health. This isn't just about numbers on a machine; it's about protecting your body's most vital organs and securing your future well-being. In this definitive guide, we will walk you through everything you need to know. You will learn:- What high blood pressure actually is and what the numbers mean.
- The hidden causes and major risk factors.
- The subtle (or non-existent) symptoms to be aware of.
- How to get a proper diagnosis and the latest treatment options.
- Actionable prevention tips you can start using today.
- Let's demystify hypertension and empower you with the knowledge to manage it effectively.
What Is High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)?
Imagine your circulatory system is a complex plumbing network. Your heart is the pump, and your arteries are the pipes that carry blood to every part of your body. Blood pressure is the force of that blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when this force is consistently too high. Over time, this constant pressure damages the delicate inner lining of your arteries, making them harder and narrower. This forces your heart to work much harder to pump blood, leading to a cascade of potential health issues.Understanding Your Blood Pressure Numbers: A Simple Breakdown
When you get your blood pressure checked, you receive two numbers, like 120/80 mmHg. Here’s what they mean:- Systolic Pressure (the top number): Measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats.
- Diastolic Pressure (the bottom number): Measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
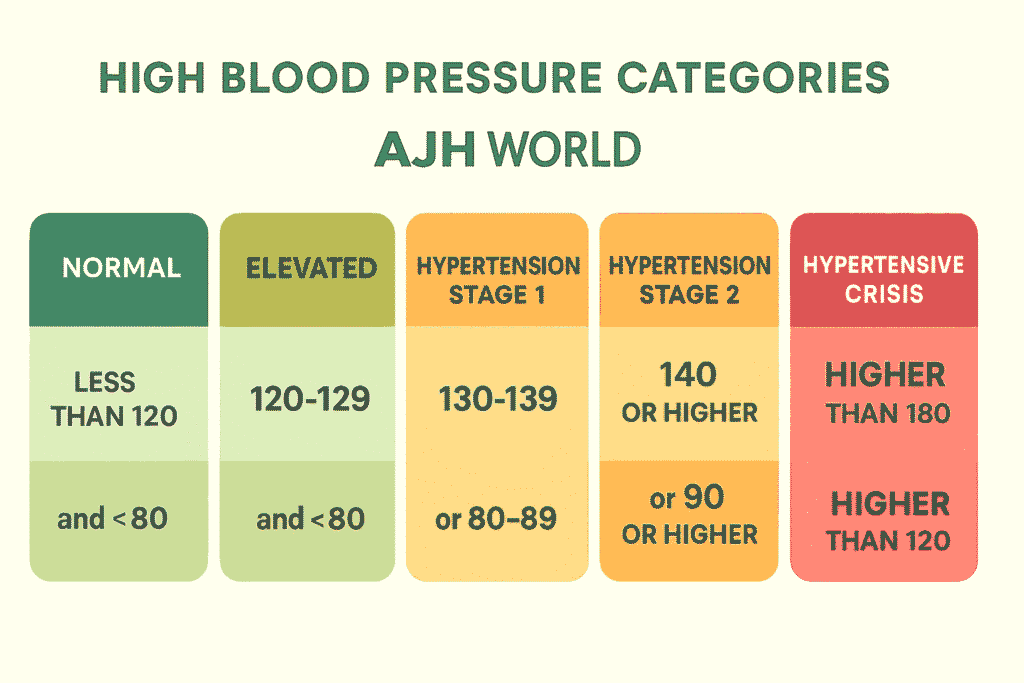
- A Hypertensive Crisis requires immediate medical attention.
Common Causes and Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure
Hypertension is generally classified into two types:Primary (Essential) Hypertension
For most adults, there's no single identifiable cause. This type of high blood pressure tends to develop gradually over many years. It's likely a combination of factors, including:- Genetics: A family history of high blood pressure increases your risk.
- Age: The risk increases as you get older.
- Race: It's particularly common among people of African heritage.
- Obesity: The more you weigh, the more blood you need to supply oxygen and nutrients to your tissues, which increases pressure on artery walls.
- High Sodium Intake: Too much salt in your diet causes your body to retain water, increasing blood volume and pressure.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Inactivity leads to a higher heart rate, making your heart work harder with each contraction.
- Chronic Stress: High levels of stress can lead to temporary, but significant, spikes in blood pressure.
Secondary Hypertension
This type is caused by an underlying condition and tends to appear suddenly, causing higher blood pressure than primary hypertension. Common causes include:- Kidney disease
- Thyroid problems
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Adrenal gland tumors
- Certain medications (e.g., birth control pills, decongestants, some prescription drugs)
Recognizing the Symptoms of High Blood Pressure (The Silent Killer)
The vast majority of people with high blood pressure have no symptoms, even if their readings are dangerously high. This is why regular screening is so vital. In the rare cases that symptoms do occur, especially during a hypertensive crisis, they might include:- Severe headaches
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Nosebleeds
- Vision changes
How Is High Blood Pressure Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is simple: a healthcare professional uses a pressure-measuring gauge with an inflatable cuff wrapped around your arm. Since blood pressure can fluctuate, a diagnosis usually isn’t made after a single high reading. Your doctor will likely take several readings over time or ask you to monitor it at home to confirm a consistent pattern of high blood pressure. (Internal Link Example): We highly recommend reading our guide on [How to Choose and Use a Home Blood Pressure Monitor] to get accurate readings between doctor's visits. Read More $1000 Credit One Bank Class Action Settlement Claim 2025 - AJH WorldEffective Treatment for High Blood Pressure
The goal of treatment is to lower your high blood pressure and protect your organs from damage. This is typically achieved through a two-pronged approach.Lifestyle Changes: The Foundation of Control
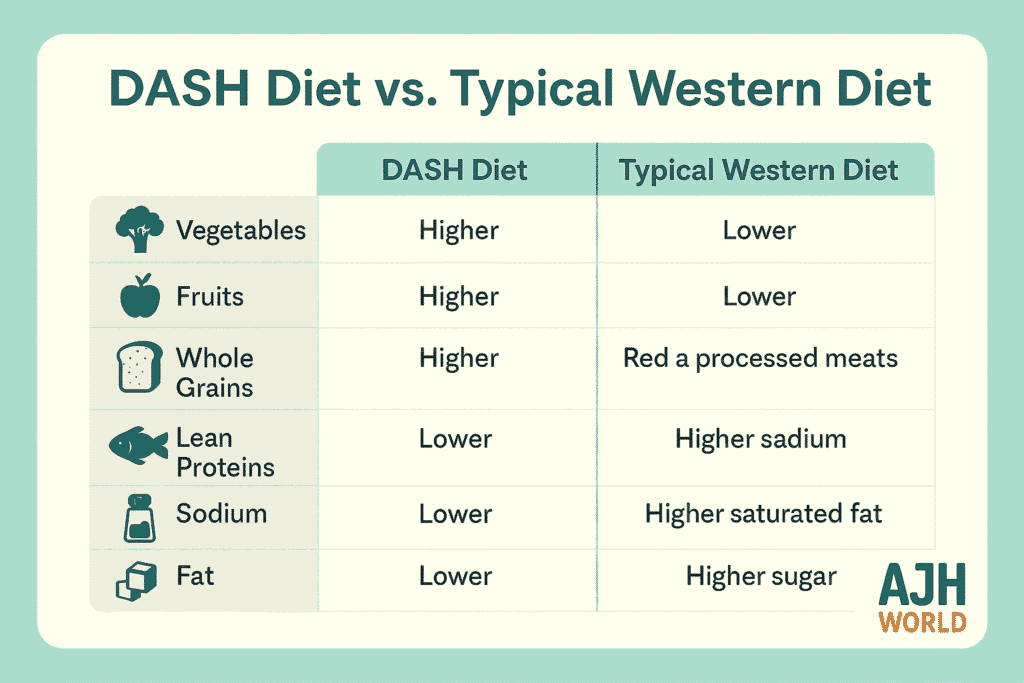
For many, lifestyle changes are incredibly effective and may be all that's needed to manage elevated blood pressure or Stage 1 hypertension.- Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet: The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Reduce Sodium: Aim for less than 1,500 mg of sodium per day. Watch out for hidden salt in processed foods, canned soups, and restaurant meals.
- Get Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, like brisk walking or cycling, per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing even a small amount of weight can make a big difference.
- Limit Alcohol: Drink in moderation.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages your blood vessels and raises your blood pressure.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation.
Medications: When Diet and Exercise Aren’t Enough
If lifestyle changes alone aren't enough to control your **high blood pressure**, your doctor may prescribe medication. Common types include: Diuretics (Water Pills): Help your kidneys eliminate sodium and water. ACE Inhibitors & ARBs: Help relax blood vessels. Beta-Blockers: Make your heart beat slower and with less force. Calcium Channel Blockers: Relax the muscles of your blood vessels. Your doctor will work with you to find the right medication or combination for your needs.Powerful Prevention: Your Proactive Guide to a Healthy Heart
Prevention is always better than cure. The very same lifestyle habits used to treat high blood pressure are the best ways to prevent it from developing in the first place. Start now, no matter your age or current blood pressure reading. Prioritize a balanced diet, stay active, manage your weight, and find healthy ways to cope with stress.2: Can I feel it if my blood pressure is high?
Usually, no. Hypertension is known as the "silent killer" because it rarely has noticeable symptoms. Relying on how you "feel" is dangerous. The only way to know for sure is to get it measured regularly.
3: What is the most common cause of high blood pressure?
For over 90% of cases (primary hypertension), there is no single, identifiable cause. It's believed to be a result of a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise habits, stress, and age.
4: Can I stop taking my blood pressure medication once my numbers are normal?
No. You should never stop taking your medication without consulting your doctor. Your numbers are likely normal because the medication is working. Stopping suddenly can cause your blood pressure to rebound to dangerous levels.
5: Can stress cause long-term high blood pressure?
While stress can cause temporary spikes in blood pressure, the direct link to long-term hypertension is still being studied by institutions like the National Institutes of Health. However, behaviors associated with chronic stress (poor diet, alcohol use, lack of sleep) are proven risk factors for high blood pressure.
Understanding High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): The Silent Killer
Nearly half of U.S. adults have high blood pressure, yet many are unaware due to its lack of symptoms. Known as the "silent killer," hypertension quietly damages the heart, blood vessels, and organs over time.
🔍 What It Is:
-
High blood pressure is the force of blood pushing too hard against artery walls.
-
Measured as systolic (top) over diastolic (bottom) (e.g., 120/80 mmHg).
📊 Blood Pressure Categories:
-
Normal: <120 / <80
-
Elevated: 120–129 / <80
-
Stage 1 Hypertension: 130–139 / 80–89
-
Stage 2 Hypertension: ≥140 / ≥90
-
Crisis: >180 / >120 (Emergency)
⚠️ Causes & Risk Factors:
-
Primary Hypertension: Age, genetics, obesity, salt intake, inactivity, stress.
-
Secondary Hypertension: Kidney disease, thyroid issues, sleep apnea, medications.
🚨 Symptoms (Usually None):
-
Rare signs: headaches, dizziness, nosebleeds, blurred vision—mostly in crises.
🩺 Diagnosis:
-
Multiple BP readings over time.
-
Home monitoring can support accurate tracking.
💊 Treatment & Management:
1. Lifestyle Changes:
-
DASH diet (fruits, veggies, low sodium)
-
Exercise (150 mins/week)
-
Weight loss
-
Limit alcohol, quit smoking, reduce stress
2. Medications (if needed):
-
Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers
🛡️ Prevention:
-
Healthy eating, regular exercise, stress management, no smoking = key prevention tools
✅ Takeaway:
High blood pressure is common but controllable. Learn your numbers, take action through lifestyle changes, and follow medical advice. Small steps lead to big health outcomes.
AJH World encourages you to share this guide and start living heart-smart today.
"AJH World" is a team of certified health writers and wellness experts dedicated to providing clear, evidence-based information to help you live a healthier, happier life. We believe that knowledge is the first step toward better health.
